machine learning 笔记
Linear Regression with one variable
Notion
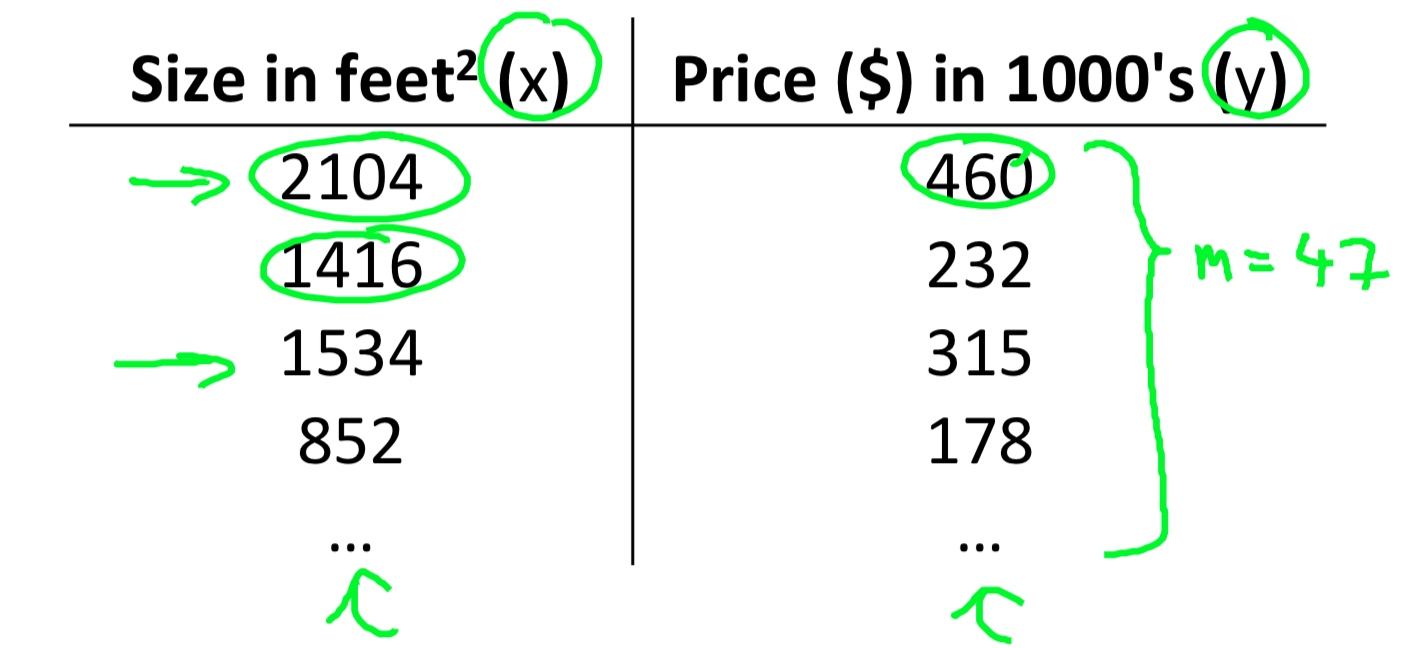
- m = Number of training examples
- x’s = “input” variable / features
- y’s = “output” variable / “target” variable
Hypothesis
\[ h_{\theta}(x) = \theta_0 + \theta_1x \]Cost function
\[ J(\theta) = \frac{1}{2m} \sum_{i=1}^m (h_\theta(x^{(i)}) - y^{(i)})^2 = \frac{1}{2m} \sum_{i=1}^m (\theta_0+\theta_1x^{(i)} - y^{(i)})^2 \]Gredient descent
\[\theta_j = \theta_j - \alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial\theta_j} J(\Theta) \\ = \theta_j - \alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial\theta_j} (\frac{1}{2m} \sum_{i=1}^m (h_\theta(x^{(i)}) - y^{(i)})^2) \\ = \theta_j - \alpha \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m (h_\theta(x^{(i)}) - y^{(i)})(x^{(i)}_j) \]- j = 0
- j = 1
(simultaneously update \(\theta_j\) for all j)
Linear Regression with multiple variables
Notion
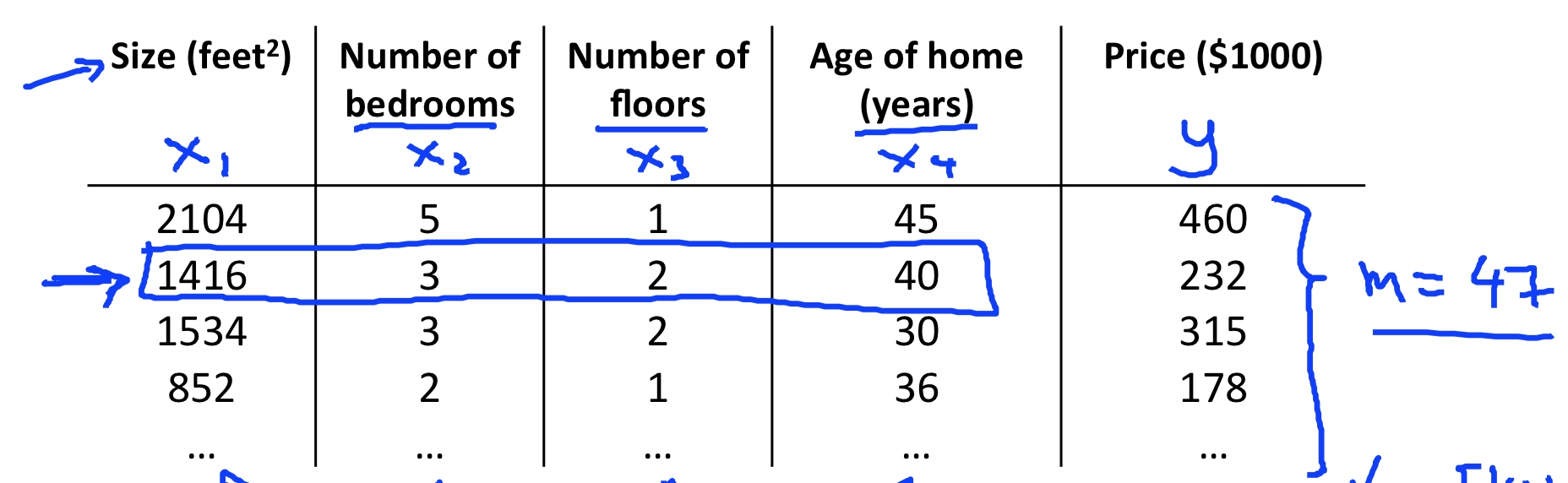
- \(n\) = number of features
- \(x^{(i)}\) = input of \(i^{th}\) training example
- \(x^{(i)}_j\) = input of \(i^{th}\) training example 's \(j^{th}\) feature.
- \(x^{(2)}_3\) = 2
Hypothesis derivation
- Previousely: \(h_{\theta}(x) = \theta_0 + \theta_1x\)
- New algorithm: \(h_{\theta}(x) = \theta_0 + \theta_1x_1 + \theta_2x_2 + \theta_3x_3\)
$
X =
\begin{bmatrix} x_0\x_1\x_2\\vdots\x_n \end{bmatrix}
\in R^{n+1}
$
$
\Theta =
\begin{bmatrix} \theta_0\\theta_1\\theta_2\\vdots\\theta_n \end{bmatrix}
\in R^{n+1}
$
- For convenience of notation, define \(x_0=1\)
$
h_{\theta}(x)
= \theta_0x_0 + \theta_1x_1 + \theta_2x_2 + \theta_3x_3
= \Theta^TX
$
Hypothesis
\[\begin{align} h_{\theta}(x) &= \Theta^TX \\ &= \theta_0x_0 + \theta_1x_1 + \theta_2x_2+ \cdots + \theta_nx_n \end{align} \]Cost function
\[\begin{align} J(\theta) &= J(\theta_0, \theta_1, \cdots, \theta_n) \\ &= \frac{1}{2m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}(h_\theta(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})^2 \end{align} \]Gradient descent
\[\begin{align} \theta_j &= \theta_j - \alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial\theta_j} J(\Theta) \\ &= \theta_j - \alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial\theta_j} (\frac{1}{2m} \sum_{i=1}^m (h_\theta(x^{(i)}) - y^{(i)})^2) \\ &= \theta_j - \alpha \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m (h_\theta(x^{(i)}) - y^{(i)})(x^{(i)}_j) \end{align} \]- j = 0
- j = 1
……
Feature Scaling
- Make sure features are on a similar scale.
- Get every feature into approximately a \(-1 \leq x_i \leq 1\) range.
Mean normalization
Replace \(x_i\) with \(x_i-\mu_i\) to make features have approximately zero mean
(Do not apply to ).
E.g.
\[ x_1 = \frac{size-1000}{2000} \] \[ x_2 = \frac{bedrooms-2}{5} \] \[x_1 = \frac{x_1-\mu_1}{\sigma_1} \] \[x_2 = \frac{x_2-\mu_2}{\sigma_2} \]Learning rate
While doing gradient decent
\[\theta_j = \theta_j - \alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial\theta_j} J(\Theta) \]“Debugging”: How to make sure gradient descent is working correctly.
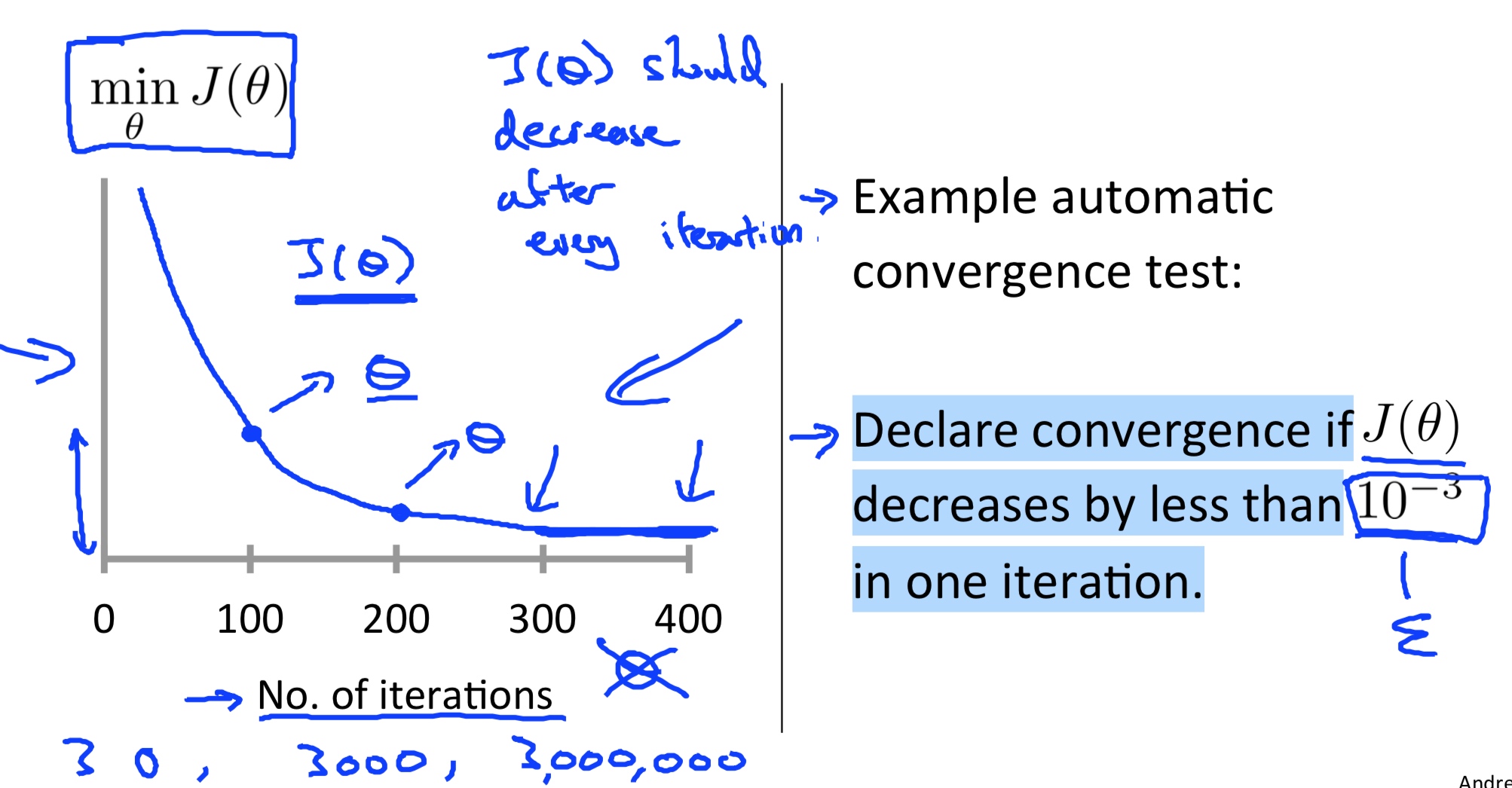
How to choose learning rate
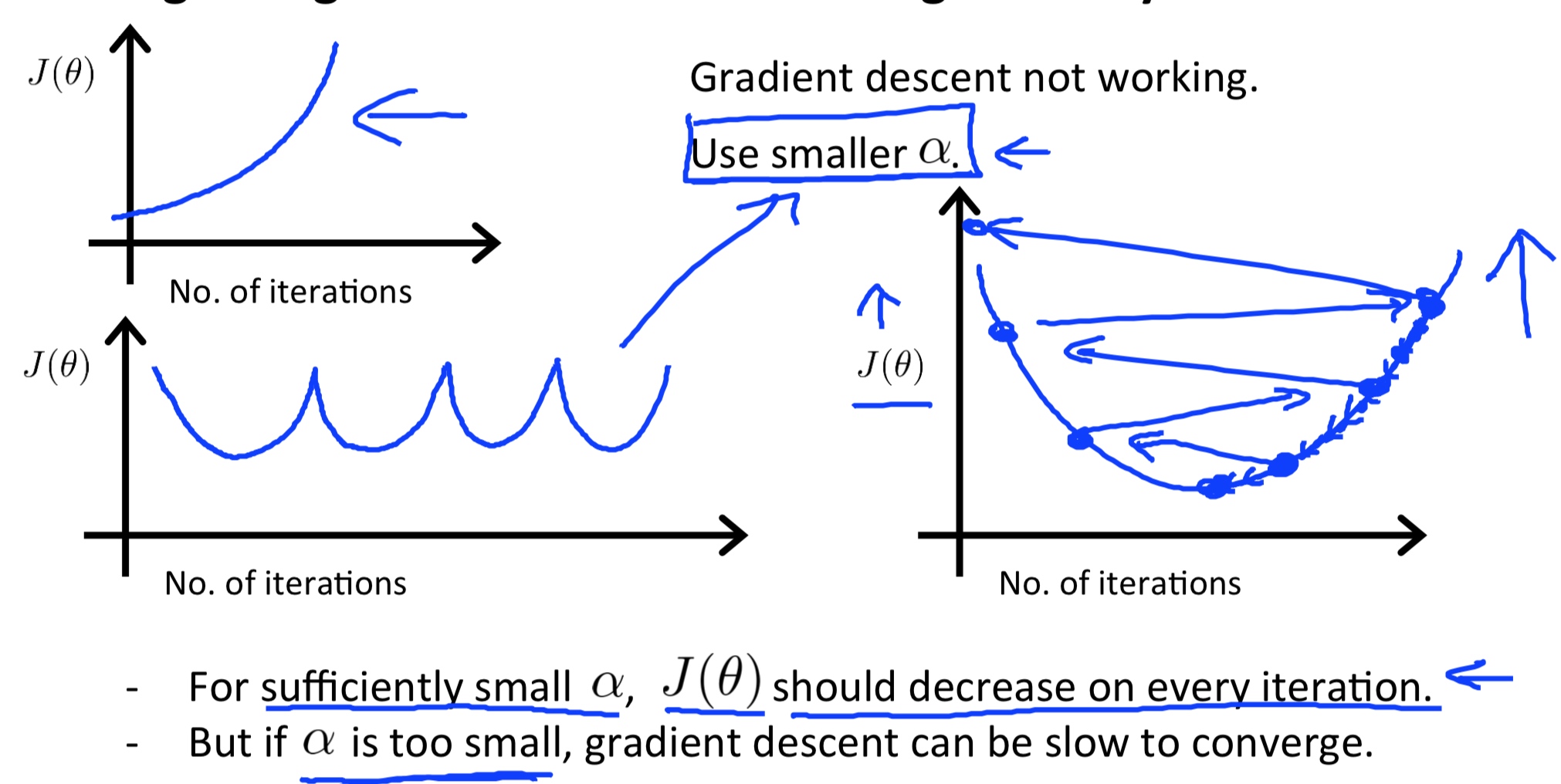
Summary:
- If \(\alpha\) too small: slow convergence
- If \(\alpha\) too large: \(J(\theta)\) may not decrease on every iteration; may not converge.
To choose \(\alpha\), try
\(\cdots, 0.001, 0.003, 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, \cdots\)
Normal Equation
Normal equation: Method to solve for analy2cally.
\[ \theta = (X^TX)^{-1}X^Ty \]| Gradient Descent | Normal Equation | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Need choose \(\alpha\) | No need to choose \(\alpha\) |
| 2 | Need many iterations | Do not need to iterate |
| 3 | Works well even n is large | Need to compute \((X^TX)^{-1}\), time complexity O(n^3) |
| 4 | Slow if n is very large |
Linear Algebra:
Matrices and vectors
- Matrix:
- Dimension of matrix:
- Matrix Elements
- Vector
Addition and scalar multiplication
Matrix Addition
Scalar Multiplication
Matrix-vector multiplication
Matrix-matrix multiplication
Matrix multiplication properties
Inverse and transpose
- Inverse
- Transponse